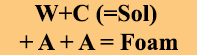CAF systems seem complicated to some people. There are a lot of little components. But most of the components exist to allow the system to produce high volume CAF for as long as needed. Some of the components exist to make the foam automatically while some components exist to keep the high-volume system cool and functioning. Understanding each component and its roll in CAF delivery will help firefighters understand the system and help the system last for years to come. Just remember the entire process is based on W + Conc + A + A = Foam (Bubbles).
The components are separated into four sections: Compressor, Hydraulic Oil System Components, Air Control Circuit Components, and Misc. Components (the parts that do not fit directly into the previous categories? The four categories are found in the drop down menu.
For the location of and relation to the various components, please reference the below diagram.